Electroplating wastewater treatment technology sharing
The electroplating industry discharges huge amounts of pollutants, which are highly toxic and difficult to treat, and can easily cause great environmental damage. Electroplating wastewater contains a large amount of heavy metals, which tend to accumulate in living organisms and are not biodegradable. Many heavy metal elements are toxic or carcinogenic and must be effectively treated before they can be discharged.
The production water for a certain electroplating wastewater treatment project that Shanqing Environment is responsible for includes water for electroplating, anodizing (including sulfuric acid anodizing, hard anodizing, and chromic acid anodizing), oxidation, chromate process, acid mist absorption treatment, and cleaning. The project water consumption is approximately 65m3 / d (4.06m3 /h), 19,500m3 / a.
According to the company, the discharge volume of chromium-containing wastewater (including acid mist absorption treatment wastewater) generated on the production line of this project is 200t/d, the discharge volume of heavy metal-containing wastewater (containing nickel and copper wastewater) is 160t/d, the discharge volume of acid-base wastewater is 150t/d, and the discharge volume of oil-containing wastewater is 100t/d.
After treatment by the sewage treatment facilities, 347t/d of chromium-containing wastewater (including acid mist absorption treatment wastewater) and heavy metal-containing wastewater (nickel and copper-containing wastewater) were reused, of which 3t/d was lost due to evaporation and crystallization during the treatment process. 185t/d of acid-base wastewater and oil-containing wastewater were reused and 65t/d were discharged.
Table 1.1 Water balance summary
/
Chromium-containing wastewater (including acid
Mist absorption wastewater treatment)
Wastewater containing heavy metals
(Wastewater containing nickel and copper)
Acid and alkaline wastewater
Oily wastewater
Domestic sewage
Catering wastewater
Water consumption m3 / d
1.6
1.4
20
45
8
5
Production volume m 3 /d
200
160
150
100
6.4
4
Recycling amount m 3 /d
198.4
158.6
130
55
/
/
Loss m 3 /d
1.6
1.4
/
/
/
/
Emissions m3 / d
0
0
20
45
6.4
4
Chapter 1 Design Conditions
2.1. Design scale
Wastewater name
Processing capacity (tons/day)
Chromium-containing wastewater
200
Heavy metal wastewater
160
Acid and alkaline wastewater
150
Oily wastewater
100
Domestic sewage
6.4
Catering wastewater
4
2.2. Emission standards
The treated electroplating wastewater is discharged into the factory sewage network after being monitored and qualified at the workshop discharge port. The water quality of the discharged water should meet the standards in Table 2 of the "Electroplating Pollutant Emission Standard" GB21900-2008, as shown in Table 1-2.
serial number
Pollutants
Standard limit
Pollutant emission monitoring location
1
Total chromium (mg/l)
1.0
Wastewater discharge outlet of workshop or production facility
2
Hexavalent chromium (mg/l)
0.2
Wastewater discharge outlet of workshop or production facility
3
Total Nickel (mg/l)
0.5
Wastewater discharge outlet of workshop or production facility
4
Total Silver (mg/l)
0.3
Wastewater discharge outlet of workshop or production facility
5
Total copper (mg/l)
0.5
Total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater
6
Total zinc (mg/l)
1.5
Total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater
7
pH
6-9
Total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater
8
Suspended matter (mg/L)
50
Total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater
9
Chemical oxygen demand (CODcr, mg/L)
80
Total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater
10
Total cyanide (mg/L)
0.3
Total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater
11
Ammonia nitrogen (mg/L)
15
Total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater
12
Total phosphorus (mg/l)
1.0
Total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater
13
Fluoride (mg/l)
10
Total discharge outlet of enterprise wastewater
Chapter 2 Process Design
3.1. Wastewater classification and water volume
Discharged wastewater is collected and treated according to its quality. There are five types of wastewater, including chromium-containing wastewater, heavy metal-containing wastewater, acid-base wastewater, oil-containing wastewater , and domestic and catering wastewater . Specifically:
Wastewater name
Classification Number
Processing capacity
(tons/day)
Design processing scale
(tons/ hour )
Chromium-containing wastewater
W1
200
10
Heavy metal wastewater
W2
160
8
Acid and alkaline wastewater
W3
150
7.5
Oily wastewater
W4
100
5
Domestic sewage + catering wastewater
W 5
10.6
1
3.2. Treatment process determination
According to the classification of discharged wastewater, the wastewater treatment system of the comprehensive wastewater treatment station is determined to be composed of the following subsystems, and classified treatment of wastewater is implemented.
a. Chromium-containing wastewater pretreatment system to treat W1 wastewater.
b. Heavy metal wastewater pretreatment system to treat W2 wastewater.
c. Acid and alkaline wastewater pretreatment system to treat W3 wastewater.
d. Oily wastewater pretreatment system, to treat W4 wastewater.
e. Domestic sewage pretreatment system, to treat W 5 wastewater.
f. High-quality reused water and zero-discharge treatment system, which can reuse and treat the pre-treated wastewater of W1, W2, W3, W4 and W5 with high quality and zero-discharge.
3.3. Process flow chart
3.4. Treatment process description
3.4.1. Chromium-containing wastewater treatment system
The chromium-containing wastewater treatment system treats wastewater discharged from the production line. The specific treatment methods are:
a.Pre-treat W1, collect wastewater into regulating tank , pump it to integrated pre-treatment equipment, adjust pH value, acidic conditions, add FeSO 4 /NaHSO 3 for reduction reaction; adjust pH value, add limestone and sodium hydroxide for alkaline precipitation reaction.
b.Add heavy metal remover for enhanced sedimentation treatment; add composite flocculant for flocculation treatment; carry out solid-liquid separation treatment through inclined plate sedimentation tank; solid-liquid separation treatment water enters intermediate water tank for subsequent treatment.
c.The inclined plate sedimentation tank separates the sludge into the sludge thickening tank, and the filter press is used to dewater the sludge, and the dehydrated sludge is transported out as hazardous waste.
3.4.2. Heavy metal wastewater treatment system
The heavy metal wastewater treatment system treats the wastewater discharged from the production line. The specific treatment methods are:
a.W2 is treated. Wastewater is collected in a regulating tank and pumped to an integrated pretreatment device to adjust the pH value for alkaline precipitation treatment;
b.Add heavy metal remover for enhanced removal treatment; add composite flocculant for flocculation treatment; carry out solid-liquid separation treatment through inclined plate sedimentation tank; the solid-liquid separation treatment water enters the intermediate water tank for subsequent treatment.
c.The inclined plate sedimentation tank separates the sludge into the sludge thickening tank, and the filter press is used to dewater the sludge, and the dewatered sludge is transported out for hazardous waste treatment.
3.4.3. Acid and alkali wastewater treatment system
The acid and alkali wastewater treatment system treats the wastewater discharged from the production line. The specific treatment methods are:
a.W3 is treated. Wastewater is collected in a regulating tank and pumped to an integrated pretreatment device to adjust the pH value for alkaline precipitation treatment;
b.Add heavy metal remover for enhanced removal treatment; add composite flocculant for flocculation treatment; carry out solid-liquid separation treatment through inclined plate sedimentation tank; the solid-liquid separation treatment water enters the intermediate water tank for subsequent treatment.
c.The inclined plate sedimentation tank separates the sludge into the sludge thickening tank, and the filter press is used to dewater the sludge, and the dewatered sludge is transported out for hazardous waste treatment.
3.4.4. Oily wastewater treatment system
a.The oily wastewater treatment system treats the wastewater discharged from the production line. The specific treatment methods are:
W4 is treated. Wastewater is collected in a regulating tank and pumped to an integrated pretreatment device to adjust the pH value; demulsifier is added to the flotation system for oil removal.
b.Add composite flocculant for flocculation treatment; carry out solid-liquid separation treatment through inclined plate sedimentation tank; solid-liquid separation treated water enters the intermediate water tank for subsequent treatment.
c.The inclined plate sedimentation tank separates the sludge into the sludge thickening tank, and the filter press is used to dewater the sludge, and the dewatered sludge is transported out for hazardous waste treatment.
3.4.5. High-quality recycled water treatment system
After pretreatment, the wastewaters of W1, W2, W3, W4 and W5 enter the intermediate water pool for water quality and water volume adjustment. After four physical filtrations of quartz sand, activated carbon, self-cleaning filter and ultrafiltration, suspended solids, colloids, viruses, etc. in the wastewater are removed, and the SDI of the effluent water quality is less than 5, which meets the reverse osmosis inlet water quality requirements. After two-stage filtration of reverse osmosis and concentrated water reverse osmosis, the inorganic salts in the water are removed, the produced water is directly reused, a small amount of concentrated water enters the triple-effect evaporation for evaporation and concentration, the distillate is reused, and a small amount of solid wastewater is transported for treatment.
There are many types of electroplating wastewater treatment technologies, but because of various problems in the management level and production process of the electroplating industry, the quality of wastewater treatment is also very different. It is difficult to meet the wastewater treatment standards by relying on only one wastewater treatment method. According to the results of sewage monitoring, it is necessary to combine multiple treatment technologies to treat sewage in order to achieve the most significant treatment effect. If you have relevant project requirements, please leave a message or send me a private message at any time.
Wastewater Treatment Technology in Yellow Rice Wine Production
A domestic rice wine production enterprise has a wastewater volume of 3500m3/d, and the wastewater discharge complies with the management standards. Based on the information provided by the owner and our company's relevant treatment experience in similar industries, Shanqing Environment has conducted a comprehensive investigation and analysis of the sewage quality and quantity, and based on the principle of "separation of clear and turbid water, and compliance with effluent standards", provided supporting water treatment solutions for the wastewater treatment station. While ensuring the treatment effect, the investment and operating costs are reduced as much as possible.
1. Design principles
▲ Design processing capacity: 3500m3/d
▲ Processing standards
The effluent quality of this project must meet the piped standard - "Water Quality Standards for Sewage Discharge into Urban Sewers", some indicators are shown in Table 2.
▲ Design principles
Based on the information provided by the owner and our company's relevant treatment experience in similar industries, and after a comprehensive investigation and analysis of the sewage quality and quantity, we provide supporting water treatment solutions for the wastewater treatment station in accordance with the principle of "separating clear and turbid water and ensuring that the effluent meets the standards".
1. Comprehensive wastewater treatment system 3500m3/d, daily recycled water 600m³, discharge 2900m³/d;
2. Use anaerobic process to produce biogas and use the biogas as a by-product of steam;
3. Choose economical, reasonable and mature processing technology;
4. The entire system adopts PLC control to realize automatic operation and management, reducing labor intensity;
5. Under the premise of ensuring the treatment effect, reduce the investment and operation costs as much as possible.
2. Process flow and process description
Figure 1 Wastewater treatment flow chart
1. Description of wastewater treatment process
01Regulating pool
The purpose is to prevent large fluctuations in water quality, water quantity and pH value, so that the structures and pipes in the treatment system are not impacted by peak wastewater flow or concentration changes, and to maintain the stable operation of the subsequent treatment system. An aeration system is installed in the pool for aeration and mixing to even out the water quality.
02Sedimentation Tank
The sedimentation tank adopts radial flow sedimentation method. Wastewater enters the tank body from the water inlet pipe in the center of the tank and flows slowly toward the periphery of the tank in the radial direction.
The suspended solids settle during the flow and enter the sludge hopper along the slope of the pool bottom, and the clarified water overflows from the pool perimeter to the canal.
A centrally driven scraper is used to collect sludge in the pool. The scraper blade scrapes the sludge that sinks to the bottom of the pool to the sludge hopper in the center of the pool, and then pumps it into the sludge thickening tank.
Radial flow sedimentation tank has the following advantages:
a. Mechanical mud discharge is adopted, the equipment is simpler and the mud discharge is smoother;
b. The method of central water inlet and peripheral water outlet causes less agitation in the water body and is more conducive to the removal of suspended solids;
03High -efficiency anaerobic reactor
The high-efficiency anaerobic reactor is a new generation of high-efficiency anaerobic reactor. Wastewater flows from bottom to top in the reactor, pollutants are adsorbed and degraded by bacteria, and purified water flows out from the top of the reactor.
04Hydrolysis Acidification Tank
The hydrolysis acidification tank is a process in which various complex organic matter in wastewater can be decomposed and converted into small molecular organic matter and other substances.
Heterotrophic bacteria in the hydrolysis acidification tank hydrolyzes suspended pollutants such as starch, fiber, carbohydrates and soluble organic matter in the sewage into organic acids, decomposes large molecular organic matter into small molecular organic matter, and converts insoluble organic matter into soluble organic matter. When these products of anoxic hydrolysis enter the aerobic tank for aerobic treatment, the biodegradability efficiency of the sewage can be improved.
05Activated sludge tank
After the wastewater passes through the hydrolysis acidification tank, it is evenly mixed and aerated in the activated sludge. The microorganisms in the water use dissolved oxygen to decompose most of the organic matter into CO2 and H2O through metabolism, effectively reducing the COD effluent value.
06 MBR Reactor
Membrane bioreactor can maximize the function of biological reaction through membrane separation technology. MBR has many technical features, compared with traditional treatment technology, including:
1. The processing system occupies a small area.
2. The system has a simple structure, convenient operation and management, and easy maintenance.
3. The structure is simple and maintenance is very simple. Daily management only requires checking the filter pressure and cleaning the aeration pipe. Cleaning the aeration pipe can also be done by simply opening and closing the valve, which is very simple.
4. High durability and long service life.
2. Wastewater discharge and reuse standards
01Wastewater Discharge Standards
02Water Reuse Standards
Shanqing Environment uses the above process to make the treated wastewater meet the discharge standards and be reused. The above case is for reference only. If you have other wastewater treatment related needs, please feel free to contact us for consultation. Shanqing Environment can provide you with more mature, reliable, efficient, energy-saving, low investment, low operating cost, and low secondary pollution water treatment processes and equipment.
Slaughterhouse Wastewater Treatment Process
1. Water quality types and characteristics
In this project comes from pen washing, leaching, slaughtering and factory floor washing, scalding, dissection, side dish processing, animal residues, blood water, etc. It has the characteristics of large water volume, uneven drainage, high concentration, many impurities and suspended solids, and good biodegradability. At the same time, the biggest difference compared with other high-concentration wastewater is that its NH3-N concentration is higher (about 120mg/L).
1.1 Design water volume
Designed water volume: 150m³/d, i.e. 7.5m³/h (daily operation time is 20 hours)
1.2 Influent water quality
According to the pollutant water quality index data provided by the owner , the designed influent water quality index of this project is shown in the following table :
Table 1 Design influent water quality index table
Monitoring Metrics
C OD
NH3-N
Water Intake Restriction
≤ 3000
≤ 75
1.3 Outlet water quality
Table 2 Designed effluent water quality index table
Monitoring Metrics
C OD
NH3-N
Emission Limits
≤ 250
≤ 25
2. Process design plan
2.1 Process
( Process flow chart )
2.2 Process Overview
Basket grille: filter out large particles in the water, such as garbage, leaves, minced meat, etc.
Pre-sedimentation regulating tank: regulate water quality and quantity.
Solid-liquid separator: separates hair, feces, etc. from wastewater.
Grease trap: removes floating oil from water.
Intermediate water pool: water storage function.
Coagulation flotation tank: by adding PAC and PAM, the tiny particles and colloids in the water are condensed into larger suspended matter under the action of the agent, and are carried to the water surface by the floating tiny dissolved air bubbles, and then scraped to the sludge tank by the scraping system to achieve solid-liquid separation . Remove suspended matter, colloids, and some organic matter in the water .
Hydrolysis acidification tank: Degrade some organic matter through hydrolysis and acidification reactions of microorganisms to improve the biodegradability of organic matter.
Two-stage A/O /precipitation system: Microorganisms degrade and remove organic matter, ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus in wastewater under alternating anoxic and aerobic environments .
Sludge treatment system : mainly composed of sludge tank and sludge dewatering system . The scum and residual sludge produced by the flotation tank, hydrolysis acidification tank and two-stage A/O /sedimentation system are discharged into the sludge tank. After further gravity concentration in the sludge tank , the sludge is pressurized by the sludge feed pump and pumped into the sludge dewatering machine to reduce the moisture content of the sludge and make the moisture content of the mud cake less than 75 %. The dehydrated sludge is outsourced for treatment .
2.3 Operation Effect and Analysis
The project started to be debugged in early 2013. After three months of system debugging, all process sections have been put into normal operation at full capacity. The monitoring and acceptance department has continuously monitored the wastewater treatment project and the water quality monitoring results are averaged. The results are shown in Table 3 .
Table 3 Inlet and outlet water quality test results
project
pH
COD/(mg.L -1 )
BOD 5 /(mg.L -1 )
SS/(mg.L -1 )
Animal and vegetable oil/(mg.L -1 )
Water Intake
7.3
2580
808
860
125
Water
7.1
50
12
15
/
It can be seen from Table 3 that all indicators of effluent are better than the first-level emission standard of "Emission Standard of Water Pollutants for Meat Processing Industry" (GB13457-1992).
3. Engineering technology and economic analysis
3.1 Technical Analysis
This process uses a combination of secondary anoxic + high-efficiency aerobic bacteria to achieve efficient nitrogen and phosphorus removal. This process can eliminate traditional anaerobic reaction units (UASB, IC) and other anaerobic reaction towers, which can reduce investment costs and land area while ensuring stable operation in the later stage.
This process has the advantages of impact resistance, high load, stable water quality and quantity, etc. Secondary anoxic treatment can not only effectively remove nitrogen and phosphorus, but also has the functions of deodorization and decolorization. This process is formed by combining traditional sewage treatment units, and has the characteristics of simplicity, stability, low technical difficulty, and easy replacement of accessories.
This process has the potential for upgrading and transformation, and the effluent water quality is high, which is convenient for effluent reuse. If multi-stage filter tanks and ultrafiltration, disinfection and other equipment are added to the end effluent, the produced water can be reused in the production line.
3.2 Operation Cost Analysis
The total investment of this project is 1.6 million yuan, of which equipment investment is 1.3 million yuan, civil engineering facilities and other investment is 300,000 yuan. It covers an area of 300m2 and can treat 150m3 of sewage per day . The specific project operation costs are: electricity fee is 0.65 yuan/m3 , chemical fee is 0.36 yuan/m3 , labor fee is 0.18 yuan/m3 , and the actual operation cost is 1.19 yuan/ m3 .
4. Conclusion
(1) Based on the high organic matter load of slaughter wastewater, flotation can be used as the pre-treatment to remove most of the grease, suspended matter, etc. The subsequent hydrolysis and acidification treatment technology can hydrolyze and acidify the large molecular organic matter in the water into small molecules, and degrade most of the insoluble organic matter into soluble substances, thereby reducing the subsequent biochemical treatment load.
(2) Highly active aerobic bacteria are added to the contact oxidation tank and highly active return sludge produced by the ordered aerobic reaction tank to adsorb most of the biodegradable organic pollutants in the sewage and effectively remove COD and BOD5 in the water.
(3) The flotation-hydrolysis acidification-contact oxidation process has been put into actual operation in multiple projects for treating slaughterhouse wastewater. The entire treatment system operates stably and has created good economic, social and environmental benefits.
Semiconductor wastewater treatment process
With the continuous changes in electronic information technology, the semiconductor technology industry has increasingly become the "heart" of development and is increasingly widely used in national economic production and life. However, the semiconductor industry is a high water-consuming industry. The more advanced the process manufacturing, the higher the requirements for its surface cleanliness, and the greater the water consumption and wastewater discharge.
For example, a semiconductor company in Beijing and a semiconductor company in Taiwan consume 1346x104㎡3 and 7000x104㎡ of water respectively, while the per capita water resources in China are 2300m2 , which is equivalent to the total domestic water consumption of a town with a population of 250,000 and 1.3 million respectively.
If the wastewater generated in semiconductor manufacturing is recycled, it will not only reduce the demand for water resources and production costs, but also reduce the emission of pollutants and the load on the environment. Shanqing Environment shared the treatment process of semiconductor wastewater containing fluorine, nitrogen, phosphorus, organic matter, heavy metal ions and acid and alkali , as well as the advantages of different processes in removing pollutants from semiconductor wastewater .
Characteristics and classification of semiconductor wastewater
1.1 Wastewater characteristics
Highly turbid and complex composition, consisting of pollutants such as fluorinated compounds, organic matter, nitrogen compounds, and heavy metal ions, and contains high levels of chemical oxygen demand (COD) And large amounts of ( silicates ) and ( aluminates ) .
(2) The strong color, high COD, high volatile organic compound content, and rich in heavy metal ions , toxic organic matter, and corrosive substances such as hydrofluoric acid make the biological degradation performance of wastewater low, and it is not suitable for treatment using traditional activated sludge method.
(3) Fluoride ions ( F - ) and fulvic acid substances can react with heavy metal ions to form stable complexes, and heavy metal ions are easy to interact with organic matter, silicate and other substances, so the pollutants in wastewater are complex and diverse.
Therefore, it is crucial to select the process and divert the treatment according to the wastewater quality type.
1.2 Wastewater classification and treatment
1.2.1 Treatment of fluoride-containing wastewater
Semiconductor fluoride-containing wastewater mainly comes from the diffusion and CMP processes in the chip manufacturing process . The current industrial applications of fluoride-containing wastewater removal methods mainly include chemical precipitation, adsorption, membrane separation , etc.
Figure 1 Fluoride-containing wastewater treatment process and its advantages and disadvantages
a.Chemical precipitation is suitable for the treatment of high-concentration fluoride-containing wastewater. Compared with other precipitants , calcium salts are relatively cheap and - The reaction generates insoluble CaF₂ . Therefore, the calcium salt precipitation method is most widely used in fluoride-containing wastewater in the semiconductor industry .
b.There are two adsorption methods: direct adsorption and electrosorption. Electrosorption, also known as capacitive deionization technology, is a method that uses charged electrodes to adsorb ions and charged particles in wastewater, so that pollutants are enriched and concentrated on the electrode surface to achieve the purpose of water purification . Traditional adsorbents in direct adsorption, such as activated carbon and clay, have problems such as low adsorption capacity, poor selectivity, secondary pollution to the environment, and poor effluent quality .
c.Membrane separation methods mainly include electrodialysis and reverse osmosis. Electrodialysis is to use the electrodes to apply a current on both sides of the selective permeable membrane to generate a potential difference, which promotes the selective permeation of anions and cations through the membrane. Reverse osmosis is to use the pressure difference on both sides of the membrane to filter water molecules and F -Method of separation.
1.2.2 Treatment of nitrogen-containing wastewater
Nitrogen-containing wastewater mainly comes from ammonia water and ammonium fluoride used in the etching process, and mainly exists in the form of ammonia nitrogen. At present, the main treatment methods for ammonia nitrogen wastewater include air stripping , adsorption, neutralization, breakpoint chlorination, biological method, etc.
picture 2 Ammonia nitrogen wastewater treatment process and its advantages and disadvantages
a.There are two types of stripping methods: air stripping and steam stripping. Compared with air stripping, steam stripping has a higher ammonia nitrogen removal rate, which can reach more than 90%, and is suitable for wastewater with higher concentrations .
b.The adsorption method is generally only applicable to low-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater. In high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater, it is often coordinated with other processes to carry out deep denitrification treatment .
c.The breakpoint chlorination denitrification process can be used for a single denitrification process or for the deep treatment of a denitrification process.
1.2.3 Treatment of phosphorus-containing wastewater
mainly comes from aluminum etching liquid in the production process. It exists in the form of PO₄³ - . The treatment methods for phosphorus-containing wastewater include chemical precipitation, biological method, adsorption method, crystallization method and ion exchange method.
picture 3 Phosphorus-containing wastewater treatment process and its advantages and disadvantages
( 1) Traditional adsorbents have problems such as high replacement cost and low adsorption capacity. Recently, many scholars have prepared high-performance adsorbents by chemically modifying low-cost industrial waste .
( 2) Compared with chemical precipitation, the precipitate produced by crystallization precipitation has a higher secondary utilization value and can be used as plant fertilizer. At the same time , it can also show good removal performance for phosphorus.
1.2.4 Treatment of organic wastewater
And CMP process in production , and mainly contains solvents such as isopropyl alcohol, propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate, acetone, xylene, etc., with high COD and low biodegradability. At present, the main treatment methods for organic wastewater include biological methods and advanced oxidation methods.
(1)bioreactors and chemical and biological combined methods are often used to treat wastewater.
( 2) The advanced oxidation treatment (AOP) process is considered to be the best method for treating organic wastewater due to its fast oxidation rate and high mineralization efficiency.
Figure 4 Organic wastewater treatment process and its advantages and disadvantages
1.2.5 Treatment of heavy metal wastewater
Heavy metal wastewater in semiconductors mainly comes from electrochemical plating ( ECP ) and CMP processes, mainly copper and cobalt, which mainly exist in the form of complexes formed by chelating agents. The main treatment methods for complexed heavy metal wastewater include adsorption, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, oxidation-reduction, etc.
Figure 5 Heavy metal wastewater treatment process and its advantages and disadvantages
( 1) Chelate precipitation is a method of removing heavy metals by using heavy metal chelating agents (such as amino and dithiocarboxyl groups) to form insoluble salts with heavy metals.
( 2) Advanced oxidation method uses strong oxidative free radicals to destroy the strong chemical bonds between heavy metal ions and certain functional groups in the ligand to release heavy metal ions.
( 3) Adsorption methods include co-removal of heavy metals and organic acids and heavy metal extraction. Organic acid co-removal technology is a process of removing pollutants from wastewater by adsorbing the entire complex onto an adsorbent .
1.2.6 Acid and alkali wastewater treatment
The semiconductor manufacturing process will discharge a large amount of acidic or alkaline substances , which will make the pH value of the wastewater too low or too high , which is easy to cause harm to the environment . At present, the treatment of this type of wastewater usually adopts three-stage neutralization technology to adjust the pH value. Value is 6.0-7.5 rear emission.
The semiconductor industry is a high water consumption industry, and wastewater recycling is one An effective way to solve the water crisis in the semiconductor industry , At present, due to cost and technical issues , wastewater with relatively good water quality can be recycled, while wastewater with relatively complex water quality can be recycled. one Generally discharged after treatment .
1000 tons/day soybean protein extraction production wastewater treatment
1. Design basic data
1.1 Design processing scale
Design the scale of comprehensive wastewater treatment: The project needs to treat 281772.6t/a (939t/d) of wastewater, the project design treatment capacity is 1000t/d, the civil engineering is expected to be designed according to the total design water volume, and the equipment is designed according to the total water volume; the land planning is 45*20 meters.
1.2 Sewage station inlet water quality
The sewage station provided by the owner needs to treat the following water quality:
According to the owner, the specific water quality of production wastewater is as follows:
1.3 Sewage station effluent quality
1.3.1 Recycled water quality
The quality of recycled water shall comply with the "Water Quality for Industrial Water Use in Urban Wastewater Recycling" (GB/T19923-2005)
The recycled water effluent from the project's production wastewater after treatment meets the requirements of Table 1 of "Water Quality for Industrial Water Use in Urban Wastewater Recycling" (GB/T19923-2024) for cold open circulating cooling water make-up water. The recyclable water volume is 210,000 m3/a. The water demand of the project's cooling circulation system is 542,700 m3/a. Therefore, the recycled water generated after the treatment of the project's production wastewater can be fully reused without being discharged.
Table 1 Recycled water is used as cooling water in the water quality standards for industrial water sources. The specific indicators are as follows:
、
1.3.2 Drainage quality
The concentrated water produced by the sewage treatment plant meets the sewage plant takeover standards and is taken over to the Jiangcheng sewage treatment plant.
The water quality of external drainage shall comply with the Class B standard in Table 1 of the Comprehensive Sewage Discharge Standard (GB8978-1996) and the Water Quality Standard for Sewage Discharge into Urban Sewers (GB/T31962-2015). The specific water discharge indicators are:
1.4 Wastewater discharge from the whole plant
2. Wastewater treatment process design
According to the characteristics of raw water, the requirements of the owner, the scale of land, and in line with the principles of economic applicability, energy conservation and emission reduction, a plan of resource treatment using advanced biochemical + membrane separation technology is proposed. After treatment, all the deep-treated product water is reused as production cooling circulating water supplement water and domestic miscellaneous water. The treatment process of this plan is designed as "air flotation + AO integration + MBR + ultrafiltration + reverse osmosis water production for cooling circulating water, and reverse osmosis concentrated water for external discharge" process.
2.1 Design processing efficiency of each process section
2.2 Wastewater treatment process flow chart
2.3 Description of core processes for wastewater treatment
2.3.1 Flotation tank
The function of flotation is to separate low-density substances such as grease in wastewater by density screening, so as to float out the lighter grease and grease, thereby achieving the separation of water and oil substances.
2.3.2AO integrated simultaneous nitrification and denitrification process
The core of the AO integrated (integrated nitroso simultaneous denitrification) process is to control the simultaneous progress of nitrification and denitrification reactions in one tank, so that the microbial flora of the two reactions can coexist in the system, thereby achieving efficient removal of ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen and COD. At the same time, it can reduce the power consumption required for aeration, and by extending the residence time, reduce the amount of residual sludge, and save sludge treatment costs.
2.3.3MBR membrane system
The effluent from the AO integrated pool directly enters the MBR membrane pool. Through the efficient interception of the membrane, all bacteria and suspension are intercepted in the membrane pool. At the same time, it can effectively intercept nitrifying bacteria, so that the nitrification reaction proceeds smoothly and NH4-N is effectively removed. At the same time, it can intercept macromolecular organic matter that is difficult to degrade, prolong its residence time in the reactor, and maximize its degradation. The sludge at the end of the membrane pool is returned to the front section through the sludge return pump, and the excess residual sludge is discharged from the system, thereby controlling the concentration and activity of the activated sludge in the system.
2.3.4 Introduction to Ultrafiltration Technology
Ultrafiltration is a pressurized membrane separation technology, that is, under a certain pressure, small molecular solutes and solvents are allowed to pass through a special membrane with a certain pore size, while large molecular solutes cannot pass through and remain on one side of the membrane, thereby partially purifying the large molecular substances. When water passes through the ultrafiltration membrane, most of the colloids and particles contained in the water can be removed, and a large amount of suspended organic matter can also be removed.
2.3.5 Reverse Osmosis Technology
Reverse osmosis is also called reverse osmosis (RO). It uses a certain pressure to separate the solvent in the solution through a reverse osmosis membrane (or semi-permeable membrane). Because it is opposite to the direction of natural osmosis, it is called reverse osmosis. According to the different osmotic pressures of various materials, the reverse osmosis method with a pressure greater than the osmotic pressure can achieve the purpose of separation, extraction, purification and concentration.
Car wash wastewater treatment process
Ⅰ Car wash wastewater treatment process
While saving costs, it meets the reuse standards and helps the car wash industry to efficiently solve the sewage problem. Shanqing Environment usually uses the following processes to treat car wash wastewater until the wastewater is recycled.
1. Processing technology
1.1 Physical processing technology:
Sedimentation method: Through the action of gravity, the suspended matter in the wastewater is naturally settled and separated from the water to achieve the purpose of purification.
Filtration method: The suspended matter in the wastewater is intercepted by filtering media to achieve the purpose of purification.
Adsorption method: Utilize the adsorption effect of adsorbents to adsorb harmful substances in wastewater on the surface to achieve purification purpose.
1.2 Chemical treatment technology:
Neutralization method: By adding acid or alkali to the wastewater, the pH value is adjusted to convert harmful substances in the wastewater into harmless substances.
Redox method: By adding oxidants or reductants to the wastewater, harmful substances in the wastewater are oxidized or reduced to harmless substances.
Coagulation method: By adding coagulants into the wastewater, the colloidal substances in the wastewater are condensed into large particles and separated by sedimentation.
1.3 Biological treatment technology:
Haoyang biological treatment: By introducing air or oxygen into the wastewater, the oxygen required for the growth of microorganisms is provided, and the metabolism of microorganisms is used to convert organic matter in the wastewater into harmless substances.
Anaerobic biological treatment: By cultivating anaerobic microorganisms under anaerobic conditions, the organic matter in the wastewater is converted into gases such as methane through their metabolism.
2. Treatment process
Process introduction: This system is designed as a 2T/h reclaimed water reuse system .
Process description: Physical methods are used to remove impurities in water, the water output is good, the equipment is easy to install, the footprint is small, and the use is economical. However, each process requires frequent backwashing, the activated carbon needs to be regenerated after a period of use, and the precision filter element also needs to be replaced regularly.
2.1 Raw water pool
The raw water pool is used to store wastewater after car washing. Some sediment will settle in the wastewater, acting as a sedimentation tank.
2.2 Raw water pressure pump
The sewage in the raw water pool is pressurized and transported to the pretreatment equipment , ensuring that the sewage has sufficient power during the filtration process .
2.3 Quartz sand filter
The quartz sand filter is used to remove large impurities such as sediment and suspended solid particles in the incoming water .
During operation, large particles of impurities are trapped on the surface of the filter layer. After a period of operation, the impurities on the surface of the filter layer will gradually increase, and the pressure difference of the filter layer will also increase. After a certain period of time, the filter layer will be penetrated and the filtering capacity of the filter layer needs to be restored through the backwashing process. Therefore, a regular backwashing program must be set during the entire automatic operation process. The frequency of backwashing depends on the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet points of the filter or the operating cycle of the filter. Under normal circumstances, we recommend that backwashing should be performed when the pressure drop value is 0.7 bar or when it runs for 24 hours.
During backwashing, the water flow direction is opposite to the running direction. The filter layer is lifted and expanded under the action of large flow backwash water. The fouling substances are separated from the filter layer along with the backwash water flow and discharged from the tank from the top, thus achieving the purpose of backwashing .
2.4 Activated carbon filter
Function and effect
Its adsorption capacity is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
⑴Can adsorb organic matter, colloidal particles and microorganisms in water;
⑵Can adsorb non-metallic substances such as chlorine, ammonia, bromine, iodine, etc.;
⑶ Can adsorb metal ions, such as silver, arsenic, bismuth, cobalt, hexavalent chromium, mercury, antimony, tin and other ions;
⑷ Can effectively remove color and odor. Filter out chemical organic matter, heavy metals, color, odor, chloride ions, etc. in water .
2.5 Security Filter
Function and effect:
The security filter is set before the ultrafiltration to prevent large particles in the water from entering the ultrafiltration membrane and ensure the normal operation of the ultrafiltration system . The security filter is a vertical columnar device with a PP spray filter element installed inside, and the filtration accuracy is 5μm. Colloid and particle fouling can seriously affect the performance of the ultrafiltration membrane element .
Features:
1. It can effectively remove suspended matter, impurities, rust and other substances in the liquid.
2. Able to withstand higher filtration pressure.
3. The unique deep mesh structure inside the security filter enables the filter element to have a higher slag load capacity.
4. The filter element can be made of a variety of materials to meet the needs of various fluid filtration.
5. The security filter has a small size, large filtration area, small resistance and long service life.
6. Resistant to acid and alkali chemical solvents, can be used in filtration equipment in the chemical industry.
7. High strength, high temperature resistance and the filter element is not easy to deform.
8. Low price, low operating cost, easy to clean the filter, convenient operation, replaceable filter element, and long filter service life.
9. Small filtration resistance, large liquid flux and strong pollution interception ability.
2.6 Ultrafiltration
Function and effect
Using new hollow fiber filtration technology, combined with three-stage pre-treatment filtration, the ultrafiltration micropore is less than 0.01 micron, which can completely filter out harmful substances such as bacteria , rust, colloids, etc. in the water. In the car wash wastewater, it mainly removes macromolecular compounds, clay, minerals, emulsion particles, microorganisms, grease, detergents, oil, and water emulsion.
2.7 Ultraviolet sterilizer
Function and effect
(Total Organic Carbon) and other residual organic matter in water . Ultraviolet light can kill 99.9% of bacteria, as well as viruses, fermentation products, mold and algae.
Car wash wastewater is reused through the "recycled water reuse" treatment process, solving the problems of recycling car wash wastewater, removing harmful substances in the water, saving water resources, and improving environmental pollution.
Collection | The fully quantitative treatment process of landfill leachate, super detailed!
The wastewater from landfill leachate has high organic matter concentration, many types of pollutants, and great changes in water quality. If these wastewaters are not effectively treated, they will pollute the water environment in the area. Shanqing Environment uses the "pretreatment and impurity removal process + inclined plate sedimentation process + air flotation to remove suspended solids + UASB hydrolysis and acidification + A0 biofilm treatment + catalytic oxidation + RO reverse osmosis" process for this type of wastewater, so that the treated wastewater meets the standards for discharge or reuse.
1. Engineering Design
Design water volume
Water volume analysis: According to the relevant information provided by the owner, the wastewater treatment facility in this plan has a treatment capacity of 200 m³ /d, running 20 hours a day, and 10 m³ /h.
Source of sewage: leachate wastewater.
Influent water quality
According to the relevant data of the same type of sewage, the wastewater quality is as follows:
Unit: mg/L (except pH)
Table 1 -1 Wastewater Influent Quality
Outlet water quality
According to the relevant standards in "Water Quality for Industrial Water Use in Urban Wastewater Recycling" (GB/T 19923-2005), the effluent can be reused for process and product water, direct cooling water, open circulating cooling water system supplementary water, washing water, etc. Specific indicators are shown in the table below:
Unit: mg/L (except pH)
Table 1 -2 Water output index table
2.Process flow and description
Figure 2-1 Process flow chart
2.1 Regulating pool
The role of regulation is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Provide buffering capacity for sewage treatment load to prevent drastic changes in treatment system load;
2. Reduce the fluctuation of sewage flow entering the treatment system, so that the feeding rate of chemicals used in sewage treatment is stable and suitable for the capacity of the feeding equipment;
3. In terms of controlling the pH value of sewage and stabilizing water quality, the neutralization capacity of different sewage can be used to reduce the consumption of chemicals in the neutralization process;
4. Prevent high concentrations of salt from directly entering the biochemical treatment system;
5. When a factory or other system temporarily stops discharging sewage, sewage can still be input into the treatment system to ensure the normal operation of the system.
2.2 Self-cleaning filter
Wastewater is lifted to a self-cleaning filter to remove particulate matter and other impurities in the wastewater, facilitating the normal operation of subsequent process equipment .
2.3 Dissolved air flotation equipment
Principle: Under certain conditions, a large amount of air is dissolved in water to form dissolved air water, which is used as the working medium. By releasing the sudden decompression and rapid release, a large number of fine bubbles (1-10 m) are generated , which adhere to the m" alum flowers " in the wastewater after the coagulation reaction , so that the flocs float up, and the floating scum and floating oil are scraped off by a special scraping device to achieve the purpose of solid-liquid separation. The treatment effect depends on the surface state, particle size and specific gravity of the treated water particles.
2.4 UASB anaerobic tower
The anaerobic biological treatment process has low energy consumption; the organic volume load is high, generally 5-10kgCOD/m³·d, and the highest can reach 30-50kgCOD/m³·d; the amount of residual sludge is small; anaerobic bacteria have low nutritional requirements, strong resistance to toxicity, and high molecular weight of degradable organic matter; strong resistance to shock loads; the produced biogas is a clean energy source.
2.5 A/O Biochemical System
2.5.1 Process characteristics
(a) The process is simple, no external carbon source and post-aeration tank are required, the original sewage is used as the carbon source, and the construction and operation costs are low;
(b) Denitrification comes first, followed by nitrification, with internal circulation, using the organic substrate in the original sewage as the carbon source, which has a good effect and a sufficient denitrification reaction.
(c) The aeration tank is at the end, so that the denitrification residues can be further removed, improving the water quality of the treated water; strong aeration is used in the front section of the O section, and the gas volume is reduced in the back section to reduce the DO content of the internal circulation liquid to ensure the anoxic state of the A section.
(d) The stirring in section A only serves to suspend the sludge but avoid the increase of DO.
2.6 MBR system
2.6.1 Working Principle
A new type of treatment system that combines biological treatment with membrane separation technology. It uses membrane separation equipment immersed in an aerobic biological pool to intercept the activated sludge and macromolecular solids in the reaction tank. It can omit the final sedimentation tank and also has microfiltration, with a longer sludge age and less sludge volume.
2.6.2 Advantages
High volumetric load , short residence time, replaces sedimentation and sand filtration, occupies a small area.
MBR membrane can completely intercept sludge, no sludge settling problem, easy system operation and maintenance.
Intercepts difficult-to-decompose high-molecular substances and effectively treats high-concentration organic wastewater.
It can intercept nitrifying bacteria, achieve complete nitrification, and effectively remove ammonia nitrogen.
It can block most pathogenic bacteria and reduce the amount of disinfectants used.
Increase initial cost, but low operating cost, still more favorable in terms of total cost.
Long sludge discharge cycle, maintain low F/M ratio, reduce sludge volume by more than 1/2 under biological autolysis.
Suitable for special pollutant treatment, interception and domestication of dominant bacteria
The sludge retention time can be quite long, and slow-growing microorganisms can be retained and multiplied, which is beneficial to special or removal of difficult to decompose pollutants.
Suspended solids and turbidity are close to zero, suitable for water recovery
2.7 Ozone system
Principle: When oxygen passes through the discharge electric field between high-voltage AC electrodes, the oxygen molecules are dissociated into oxygen atoms under the bombardment of high-speed electron flow, and the oxygen atoms quickly react with oxygen molecules to form ozone molecules.
2.8 RO system
Figure 2-8-1 Reverse Osmosis Principle
2.8.1 Membrane Module
Reverse osmosis is the actuator of the entire desalination system, and its function is to remove soluble salts, colloids, organic matter and microorganisms from water. The reverse osmosis membrane of this system adopts a new type of polyamide composite membrane with large flux, anti-pollution and corrosion resistance.
The increase in water production is achieved by increasing the membrane area, rather than increasing the membrane flux and water supply pressure, so it can maintain a low fouling rate. In addition, it can maintain a high flow rate for a long time and extend the life of the membrane. The low operating pressure can enhance the operating economy of the system. The increase in membrane area can make the newly designed reverse osmosis system use fewer components, making the system more compact and saving installation costs.
Figure 2-8-1 Reverse Osmosis Device
The reverse osmosis device is the heart of the pre-desalting process of the project. Water treated by the reverse osmosis device can remove most of the impurities such as inorganic salts, organic matter, microorganisms, bacteria, etc.
Shanqing Environment uses the above process to treat 200 tons /day of landfill leachate wastewater to meet the discharge standards or reuse. The above case is for reference only. If you have other wastewater treatment related needs, please feel free to contact us for consultation. Shanqing Environment can provide you with more mature, reliable, efficient, energy-saving, low investment, low operating cost, and low secondary pollution water treatment processes and equipment.
How to treat aquaculture wastewater? Let's take a look at this process
Aquaculture wastewater is rich in organic matter, pathogens and nutrients (such as nitrogen and phosphorus). Direct discharge will lead to eutrophication of water bodies, causing problems such as water hypoxia and death of aquatic organisms. In addition, pathogens and viruses in wastewater will spread with the water flow, which may lead to the outbreak of epidemics.
Shanqing Environment has confirmed in previous engineering practices that biochemical treatment of fecal wastewater from large and medium-sized pig farms after solid-liquid separation is feasible and efficient, and for smaller scale farms, a combination of hydrolysis and acidification and aerobic treatment is more appropriate.
1. Overview of aquaculture wastewater
The types of wastewater discharged from farms include: fecal wastewater, industrial wastewater, and domestic wastewater.
Estimation of wastewater from livestock farms:
1. Water volume: 18-37 liters/(day/head) for domestic pigs, 56-256 liters/(day/head) for cattle and sheep;
2. Suspended solids in wastewater: 15-30g/L for domestic pigs, 30-50g/L for cattle and sheep;
3. COD in wastewater: 15-30g/L for domestic pigs, 35-60g/L for cattle and sheep;
4. The BOD5 in wastewater is 6.25-12.5 g/L for domestic pigs and 4-6.7 g/L for cattle and sheep;
In addition, it also contains a large amount of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.
1.1 Main Features
Aquaculture wastewater has the typical "three high" characteristics, namely: high COD (3000-12000mg/L), high ammonia nitrogen (800-2200mg/L), and high SS (exceeding the standard by dozens of times, dark color, and containing a large number of bacteria, high ammonia nitrogen and organic phosphorus content).
1.2 Advantages
It has good biodegradability, concentrated flushing and discharge time, and large impact load.
According to the characteristics of water quality, the coagulation and sedimentation process is used to remove suspended matter and color first; biochemical treatment is used to remove organic matter , ammonia nitrogen and organic phosphorus.
2. Treatment process
2.1 Common treatment processes
Engineering practice has confirmed that biochemical treatment of fecal wastewater from large and medium-sized pig farms after solid-liquid separation is feasible and efficient. For small-scale farms, a method combining hydrolysis and acidification with aerobic treatment is more appropriate.
The use of anaerobic digestion can, on the one hand, reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs; on the other hand, it can also recover and utilize methane gas, thereby achieving the purpose of waste utilization.
Biochemical treatment generally uses biofilm method for similar scale sewage treatment. It generally includes fixed bed biofilm method (contact oxidation), MBR suspended carrier biofilm method, fluidized bed, aerated biological filter, biological rotary disc, membrane bioreactor, etc.
2.2 Features
Bio-rotating disc: generally used in large-scale above-ground treatment facilities, it occupies a large area, has poor efficiency, and is prone to secondary pollution;
Membrane bioreactor membrane: difficult to replace, short life, and troublesome to clean;
Aerated biological filter: Although it is more suitable for the treatment of aquaculture wastewater and has many successful experiences, it is not recommended to use it here because of its high noise, the need for a special fan, and the small amount of water in this project;
Contact oxidation combined with high-efficiency new biological filler: It has the characteristics of high load, easy biofilm formation, and mature technology, so contact oxidation technology is used as the main treatment unit in this plan.
To sum up, based on the characteristics of pig farm wastewater, we choose "three-stage sedimentation + flotation machine pretreatment + Bardenpho + filtration + disinfection" as the treatment process for this type of wastewater.
2.3 Introduction to sewage treatment process
The biogas slurry first enters the tertiary sedimentation tank to initially precipitate the heavier suspended matter to reduce the load for subsequent treatment. The supernatant after sedimentation enters the regulating tank. The main function of the regulating tank is to balance the water quality and quantity so that the system can operate under a relatively stable condition.
The water in the equalization tank is pumped into the mixing area of the flotation after the sewage is reacted with the dosing agent, and then mixed with the released dissolved air water, so that the floccules adhere to the tiny bubbles and then enter the flotation area.
The floccules float to the water surface under the action of air buoyancy to form scum. When the scum on the water surface accumulates to a certain thickness, it is scraped into the air flotation machine sludge tank by the scraper and then discharged into the sludge tank. Part of the clean water in the lower layer flows back to be used for dissolved air, and part of it enters the clean water tank, and then enters the biochemical system under the action of the pump.
The biochemical sewage treatment system consists of (hydrolysis acidification tank, primary contact oxidation tank, secondary contact oxidation tank, sedimentation tank). The sewage is acidified in the hydrolysis acidification tank. Through hydrolysis and under the action of acid-producing bacteria, the large-molecule, difficult-to-degrade organic matter in the wastewater is decomposed into small-molecule organic matter, part of the COD and soluble organic acids are removed, and the water quality and water volume of the wastewater are adjusted to ensure the stability of the subsequent treatment load.
It flows into the biological contact oxidation tank through the hydrolysis acidification tank for biochemical reaction. Under the condition of sufficient oxygen supply, the aerobic microorganisms in the biological contact oxidation tank use the organic matter in the sewage as nutrition and carry out their own metabolic activities by decomposing and absorbing the organic matter, thereby achieving the effect of removing the organic matter in the sewage.
In order to ensure the aerobic treatment effect, diaphragm aerators and elastic three-dimensional fillers are installed in the system. The equipment converts ammonia nitrogen and other components into nitrogen and ammonia through aeration. The equipment adds elastic fillers to improve the aerobic effect and increase the area of the biofilm, increase the biomass in the aeration tank, and improve the organic matter removal rate. It has the characteristics of stable treatment effect, high volumetric load, low sludge yield, and low moisture content of residual sludge.
A certain concentration of activated sludge must be maintained in the biological contact oxidation pond, and the sludge source must be returned from the sedimentation tank. This ensures the stable operation of the entire system, maintains a high organic matter removal rate, and effectively prevents sludge swelling.
The mud-water mixture after aerobic treatment enters the secondary sedimentation tank, where the mud-water mixture is separated from the water. The precipitated sludge is returned to the hydrolysis acidification tank for denitrification reaction to remove ammonia nitrogen in the sewage. The remaining sludge is discharged into the sludge pool. The treated sludge can be entrusted for external transportation and disposal.
Through the above process, the harm of aquaculture wastewater to the environment can be effectively reduced to protect the ecological environment and human health. Shanqing Environment can provide technical solutions, equipment supply and installation and commissioning services related to aquaculture wastewater treatment. If you have any questions about aquaculture wastewater treatment, please feel free to contact us for consultation.
How to achieve zero discharge of recycled water for 220 tons/day of coconut wastewater?
Coconut industry wastewater mainly comes from various links of coconut processing industry. The wastewater of this project comes from the effluent of the previous water treatment system. The wastewater has poor biodegradability, high oil and grease content, high concentration of nitrate and phosphate, and a certain amount of ammonia and surfactant.
If these wastewaters are discharged directly without treatment, they will cause serious pollution to the water quality of the receiving water bodies and cannot be recycled.
Entrusted by an overseas client company, Shanqing Environment is responsible for scheme design, equipment selection, installation guidance, commissioning, training and other work in this project to ensure that the effluent meets the relevant standards and that the treated water can be reused for process and product water, direct cooling water, open circulating cooling water system make-up water, washing water and other purposes.
一、Design conditions
1.1 Design water volume
According to the relevant information provided by the customer, the treatment capacity of the sewage treatment facility of this project is 40 gpm, that is: 10 tons/hour, 220 tons/day.
1.2 Influent water quality
The source of sewage is the effluent from the coconut industry after pretreatment. Combined with the relevant information provided by the customer , the inlet water quality parameters are as follows.
1.3 Outlet water quality
According to the relevant standards in "Water Quality for Industrial Water Use in Urban Wastewater Recycling" (GB/T 19923-2005), the effluent can be reused for process and product water, direct cooling water, make-up water for open circulating cooling water systems, washing water, etc.
2. Process
The wastewater of this project comes from the effluent of the existing coconut wastewater treatment system. It is planned to treat the wastewater with zero discharge for reuse. In view of the characteristics of the water quality, Shanqing Environment will send the wastewater through the collection pipe to the regulating tank. After the water quality is homogenized, it will enter the ozone oxidation tower through the regulating tank lifting pump. The wastewater in the ozone catalytic tower contains a large amount of hydroxyl free radicals, which have extremely strong oxidizing properties and can break the chains of high-molecular organic pollutants, reduce COD indicators, and achieve integrated influent biochemical indicators.
After the wastewater has completed the integrated biochemical reaction, the effluent passes through a quartz sand filter to remove remaining suspended matter, and then is disinfected to meet the reuse water standards.
Figure 1 Process flow chart
2.1 Process description:
(1) In view of the water quality of the wastewater inlet of this project, the sewage will be introduced into the equalization tank for equalization and regulation before entering the main treatment body, so that its water volume and water quality are relatively stable, so as to provide a stable and optimized operating condition for the subsequent water treatment system.
(2) Ozone oxidation tower
Ozone advanced oxidation technology can decompose and oxidize organic matter that is difficult to treat by traditional biochemical methods.
Ozone destroys the complex chemical structure of these substances through oxidation, converting them into small molecular organic compounds that are easier for microorganisms to degrade, thereby improving their removal efficiency in subsequent biochemical treatments while ensuring the normal operation of biochemical treatments.
(3) Biological contact oxidation pond
The biological contact oxidation tank can remove residual organic matter and ammonia nitrogen in the water in a relatively short time. After the wastewater is treated with ozone oxidation, it enters the biological contact oxidation tank, where organic substances such as oils and sugars in the wastewater can be efficiently degraded, thereby reducing the concentration of COD, oils, ammonia nitrogen, etc. in the wastewater. The biological contact oxidation tank and the secondary sedimentation tank are combined into an integrated device.
(4) Quartz sand filter
The quartz sand filter is a water treatment device that uses quartz sand as the main filter medium and is used to remove impurities such as suspended matter, colloids, and silt in water. After biochemical treatment, the wastewater enters the quartz sand filter, which can effectively remove solid suspended matter in the wastewater, and further remove the organic matter content in the wastewater, reducing the COD value, ammonia nitrogen and sulfate concentrations.
(5) Sodium hypochlorite generator
Sodium hypochlorite generator is a water treatment disinfection and sterilization equipment. It uses salt water as raw material and produces sodium hypochlorite solution through electrolysis reaction. Sodium hypochlorite has strong oxidizing properties and can be hydrolyzed to produce hypochlorous acid with strong oxidizing properties, which can effectively kill bacteria in treated water and ensure the quality of recycled water.
Shanqing Environment uses the above process to make the treated wastewater meet the discharge standards and be reused . The above cases and processes are for reference only. If you have other wastewater treatment related needs, please feel free to contact us for consultation. Shanqing Environment can provide you with more mature, reliable, efficient, energy-saving, low investment, low operating cost, and low secondary pollution water treatment processes and equipment.
Is it difficult to treat aquaculture wastewater? Choosing the right process is the key
Aquaculture wastewater is rich in organic matter, pathogens and nutrients (such as nitrogen and phosphorus). Direct discharge will lead to eutrophication of water bodies, causing problems such as water hypoxia and death of aquatic organisms. In addition, pathogens and viruses in wastewater will spread with the water flow, which may lead to the outbreak of epidemics.
Shanqing Environment has confirmed in previous engineering practices that biochemical treatment of fecal wastewater from large and medium-sized pig farms after solid-liquid separation is feasible and efficient, but for smaller scale farms, a combination of hydrolysis and acidification and aerobic treatment is more appropriate.
1. Overview of aquaculture wastewater
The types of wastewater discharged from farms include: fecal wastewater, industrial wastewater, and domestic wastewater.
Estimation of wastewater from livestock farms:
1. Water volume: 18-37 liters/(day/head) for domestic pigs, 56-256 liters/(day/head) for cattle and sheep;
2. Suspended solids in wastewater: 15-30g/L for domestic pigs, 30-50g/L for cattle and sheep;
3. COD in wastewater: 15-30g/L for domestic pigs, 35-60g/L for cattle and sheep,
4. The BOD5 in wastewater is 6.25-12.5 g/L for domestic pigs and 4-6.7 g/L for cattle and sheep.
In addition, it also contains a large amount of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.
1.1 Main features:
Aquaculture wastewater has the typical "three high" characteristics, namely: high COD (3000-12000mg/L), high ammonia nitrogen (800-2200mg/L), and high SS (exceeding the standard by dozens of times, dark color, and containing a large number of bacteria, high ammonia nitrogen and organic phosphorus content).
1. 2 Advantages:
It has good biodegradability, concentrated flushing and discharge time, and large impact load.
According to the characteristics of water quality, the coagulation and sedimentation process is used to first remove suspended matter and color; biochemical treatment is used to remove organic matter, ammonia nitrogen and organic phosphorus.
2. Processing technology
2.1 Common processing technology:
Engineering practice has confirmed that biochemical treatment of fecal wastewater from large and medium-sized pig farms after solid-liquid separation is feasible and efficient. For small-scale farms, a method combining hydrolysis and acidification with aerobic treatment is more appropriate.
The use of anaerobic digestion can, on the one hand, reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs; on the other hand, it can also recover and utilize methane gas, thereby achieving the purpose of waste utilization.
Biochemical treatment generally uses biofilm method to treat aquaculture wastewater. It generally includes fixed bed biofilm method (contact oxidation), MBR suspended carrier biofilm method, fluidized bed, aerated biological filter, biological rotary disc, membrane bioreactor, etc.
2.2 The characteristics are:
Bio-rotating disc: generally used in large-scale above-ground treatment facilities, it occupies a large area, has poor efficiency, and is prone to secondary pollution;
Membrane bioreactor membrane: difficult to replace, short life, and troublesome to clean;
Aerated biological filter: Although it is more suitable for the treatment of aquaculture wastewater and has many successful experiences, it is not recommended to use it here because of its high noise, the need for a special fan, and the small amount of water in this project;
Contact oxidation combined with high-efficiency new biological filler: It has the characteristics of high load, easy biofilm formation, and mature technology, so contact oxidation technology is used as the main treatment unit in this plan.
To sum up, based on the characteristics of pig farm wastewater, we choose "three-stage sedimentation + flotation machine pretreatment + Bardenpho + filtration + disinfection" as the treatment process for this type of wastewater.
2.3 Introduction to sewage treatment process
The biogas slurry first enters the tertiary sedimentation tank to initially precipitate the heavier suspended matter to reduce the load for subsequent treatment. The supernatant after sedimentation enters the regulating tank. The main function of the regulating tank is to balance the water quality and quantity so that the system can operate under a relatively stable condition.
The water in the equalization tank is pumped into the mixing area of the flotation after the sewage is reacted with the dosing agent, and then mixed with the released dissolved air water, so that the floccules adhere to the tiny bubbles and then enter the flotation area.
The floccules float to the water surface under the action of air buoyancy to form scum. When the scum on the water surface accumulates to a certain thickness, it is scraped into the air flotation machine sludge tank by the scraper and then discharged into the sludge tank. Part of the clean water in the lower layer flows back to be used for dissolved air, and part of it enters the clean water tank, and then enters the biochemical system under the action of the pump.
The biochemical sewage treatment system consists of (hydrolysis acidification tank, primary contact oxidation tank, secondary contact oxidation tank, sedimentation tank). The sewage is acidified in the hydrolysis acidification tank. Through hydrolysis and under the action of acid-producing bacteria, the large-molecule, difficult-to-degrade organic matter in the wastewater is decomposed into small-molecule organic matter, part of the COD and soluble organic acids are removed, and the water quality and water volume of the wastewater are adjusted to ensure the stability of the subsequent treatment load.
It flows into the biological contact oxidation tank through the hydrolysis acidification tank for biochemical reaction. Under the condition of sufficient oxygen supply, the aerobic microorganisms in the biological contact oxidation tank use the organic matter in the sewage as nutrition and carry out their own metabolic activities by decomposing and absorbing the organic matter, thereby achieving the effect of removing the organic matter in the sewage.
In order to ensure the aerobic treatment effect, diaphragm aerators and elastic three-dimensional fillers are installed in the system. The equipment converts ammonia nitrogen and other components into nitrogen and ammonia through aeration. The equipment adds elastic fillers to improve the aerobic effect and increase the area of the biofilm, increase the biomass in the aeration tank, and improve the organic matter removal rate. It has the characteristics of stable treatment effect, high volumetric load, low sludge yield, and low moisture content of residual sludge.
A certain concentration of activated sludge must be maintained in the biological contact oxidation pond, and the sludge source must be returned from the sedimentation tank. This ensures the stable operation of the entire system, maintains a high organic matter removal rate, and effectively prevents sludge swelling.
The mud-water mixture after aerobic treatment enters the secondary sedimentation tank, where the mud-water mixture is separated from the water. The precipitated sludge is returned to the hydrolysis acidification tank for denitrification reaction to remove ammonia nitrogen in the sewage. The remaining sludge is discharged into the sludge pool. The treated sludge can be entrusted for external transportation and disposal.
Through the above process, the harm of aquaculture wastewater to the environment can be effectively reduced to protect the ecological environment and human health. Shanqing Environment can provide technical solutions, equipment supply and installation and commissioning services related to aquaculture wastewater treatment. If you have any questions about aquaculture wastewater treatment, please feel free to contact us for consultation.
Membrane Desalination Case Process Analysis
1. Process
2. Pretreatment process
Impurities in seawater: According to their size, they can be divided into dissolved matter, colloids and suspended matter.
(1) Coagulation and sedimentation: folded plate flocculation + inclined tube sedimentation
Through experimental research on the treatment effects of different coagulant dosages and no coagulant dosage, and combining engineering experience with current water quality conditions, ferric chloride was selected as an economical and applicable coagulant with a dosage of 3ppm and a water turbidity of less than 4NTU.
Adopt tubular static mixer: directly installed on the water inlet pipe, the mixing efficiency can reach more than 94%.
A folded plate flocculation tank with enhanced coagulation effect is used: the flocculation time is short and the tank volume is small.
Use a heterogeneous flow inclined tube sedimentation tank: the advantages are high sedimentation efficiency, small tank body and small footprint.
The sedimentation tank and reaction tank are built together, with a total designed water volume of 2900m3/h.
• Total flocculation time: t=22min.
• Sedimentation tank surface load: 5.5m3/m2·h.
• Water turbidity ≤5NTU
(2) Valveless filter
By utilizing high-level water inlet and outlet and siphon backwashing process, there is no need to add power equipment. It has the advantages of low cost, energy saving, simple operation and management, and the fine filtration can meet the requirements.
The valveless filter is used in conjunction with the clarifier, and is mainly composed of a top flushing water tank, a middle filter chamber, a bottom water collection chamber, a water inlet device and a flushing siphon device.
8 valveless filters are configured and divided into two groups. The overall dimensions of each valveless filter are 10.5 meters × 5.5 meters. The interior has a double-chamber structure and is filled with anthracite and quartz sand filter media. The single-chamber filtration area is 4.7 meters × 4.7 meters. The designed filtration rate is 7.3m/h. The water output of each valveless filter is about 370m3/h, and the turbidity of the produced water is ≤1NTU. The effluent flows directly into the clear water tank using the high head difference.
The effluent quality of the valveless filter is slightly lower than that of the V-type filter, but it can fully meet the requirements of the mechanical filter. The operation of the first phase for more than 8 years shows that the valveless filter is simple to operate and manage, has low failure rate, and saves maintenance costs, making it very suitable as a pre-treatment for mechanical filters.
(3) Mechanical filter
44 vertical mechanical filters are configured, with a water output of 2640m3/h. Each is a Φ3200 vertical mechanical filter, with a designed flow rate of 7.5m/h and an output of 60m3/h.
Each filter is equipped with a flow meter, inlet and outlet water pressure instruments and manual/pneumatic regulating valves. The filter is filled with quartz sand and anthracite of different grades. Seawater is filtered through the filter material, and the outlet water SDI value is less than 5, meeting the inlet water quality requirements of the reverse osmosis membrane element.
3. Desalination process
The reverse osmosis system is divided into 5 sets, each with a capacity of 5000m3/d. Through model analysis and experimental verification, the RO membrane stack combination structure is designed as an 8×8 vertical and horizontal arrangement.
3.1 The membrane stack combination adopts the large opening interface connection of the membrane shell, and the raw water or concentrated water interfaces of multiple large opening membrane shells are connected in series using copy forests. In order to ensure the convenience of disassembly and installation of the membrane stack, each branch pipe is connected to the main pipe with a double copy forest.
3.2 This structure makes the membrane stack compact, the water distribution more uniform, the disassembly and installation more convenient, and reduces the construction cost.
3.3 Through continuous monitoring of the produced water quality since operation, the water quality of the equipment is stable, safe and reliable.
In the entire membrane stack system, the 21 rows of membrane shells arranged vertically have relatively uniform water conductivity, and the difference between the membrane shells in each row is kept within 20%. The 6 rows of membrane shells arranged horizontally also have relatively uniform water conductivity, and the difference between the water conductivity of the membrane shells in each row is also kept within 20%, which further verifies that the water distribution method of the middle water inlet is relatively reasonable.
4. Energy recovery
The water production rate of this seawater desalination system is 40%, and the remaining 60% of the seawater becomes high-pressure concentrated seawater. The energy recovery device uses high-pressure concentrated water to pressurize the feed seawater, which can reduce the capacity of the high-pressure pump by 55-60%, reduce the energy consumption of seawater desalination by about 50%, and reduce the energy consumption per ton of water to below 2.2 degrees.
5. Post-mineralization treatment
This project adopts the dissolved mineral method and, through a large number of static and dynamic test studies, adds CO2 and calcium carbonate to the RO produced water to make the water quality meet the requirements.
The design process is to inject CO2 by increasing the pressure in the RO water production pipeline. CO2 reacts positively with the permeate, causing the pH value of the permeate to be acidic.
The permeate then flows by gravity into the post-mineralization tank filled with calcium carbonate particles, causing the CO2 dissolved in the water and free in the pipeline to react with the calcium carbonate particles, thereby increasing the alkalinity and hardness of the reverse osmosis water.
Solar Desalination Technology
By closely combining the solar desalination system with conventional modern desalination technology, drawing on its advanced manufacturing process and achievements in enhanced heat and mass transfer, and complementing the advantages of solar energy itself, a more ideal effect can be achieved.
1. Solar desalination technology
Traditional desalination technology requires high investment and consumes too much energy, with the energy mainly coming from fossil fuels such as oil and coal, making it difficult to promote desalination technology.
Data studies have shown that a seawater purification system with a daily output of 1,000 cubic meters of fresh water consumes 10,000 tons of oil per year. For areas lacking fossil fuel resources, especially some remote areas with low population density and no large-scale connection to the power grid, it is difficult to build traditional seawater desalination equipment. Therefore, using ubiquitous solar energy to desalinate seawater and brackish water is not the best choice.
The solar desalination system is actually a combination of solar energy utilization devices and traditional desalination devices, using solar energy instead of traditional energy to supply the energy required by the desalination device.
Some of the combinations are shown in Table 1
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of solar desalination
Figure 2 Trough solar concentrating thermal system
The trough solar thermal system has the characteristics of large scale, long life and low cost, and is currently the most mature large-scale solar thermal utilization technology. There are three main ways to produce steam for trough solar desalination: flash evaporation, direct evaporation and indirect evaporation.
1.1 Application of multi-stage flash evaporation
The direct evaporation method may have operational stability problems. Flow instability can lead to flow loss in the affected pipe section and even cause overheating of the collector tube and permanent damage to the selective absorption coating.
For the indirect evaporation method, the main disadvantage of the system is that most heat transfer fluids have special properties such as being difficult to prepare, flammable, and easily decomposed.
flash evaporation system can effectively avoid the above defects, and has the advantages of simple structure, stable operation, high efficiency and low construction cost. Therefore, the flash evaporation system is suitable as a research and development object.
Figure 3 Principle of solar flash evaporation
1.2 Characteristics of multi-stage flash evaporation
It has the advantages of high reliability, good anti-scaling performance and easy large-scale development.
At present, 60% of the global seawater desalination output is obtained by the multi-stage flash evaporation method. At the same time, multi-stage flash evaporation is also the seawater desalination method with the largest single-unit capacity (up to 100,000t/day), which is suitable for large and ultra-large desalination plants.
1.3 Working principle and process of multi-stage flash evaporation
The principle of the multi-stage flash evaporation process is as follows: the raw seawater is heated to a certain temperature and then introduced into the flash chamber. Since the pressure in the flash chamber is controlled to be lower than the saturated vapor pressure corresponding to the temperature of the hot brine, the hot brine becomes superheated water after entering the flash chamber and is rapidly partially vaporized, thereby reducing the temperature of the hot brine itself. The generated steam is condensed to become the required fresh water.
Multi-stage flash evaporation is based on this principle, whereby hot brine flows through a number of flash chambers with gradually decreasing pressures, evaporating and cooling step by step. At the same time, the brine is gradually concentrated until its temperature approaches (but is higher than) the natural seawater temperature.
The process flow of the multi-stage flash evaporation system is shown in Figure 3 above. The main equipment includes brine heater, heat recovery section of the multi-stage flash evaporation device, heat exhaust section, seawater pretreatment device, vacuum system of the non-condensable gas exhaust device, brine circulation pump and inlet and outlet water pumps, etc.
2. Basic process parameters
(1) Circulating brine flow rate
The characteristic of multi-stage flash evaporation is that it relies on the circulating brine to continuously cool down through multiple stages, releasing its own sensible heat, thereby vaporizing part of the water in the superheated brine to achieve the purpose of producing fresh water and concentrated brine.
Therefore, from the perspective of heat balance, the sensible heat released by each stage of the circulating brine is equal to the latent heat required for the generated fresh water. Therefore, for the entire multi-stage flash evaporation system, the following relationship exists: RS(t0-tn) = DL
Where, R is the circulating brine flow rate (kg/h);
S-average specific heat of salt water (kcal/kg·℃);
t0: first stage inlet temperature of circulating brine (℃);
tn-the final outlet temperature of circulating brine (℃);
D-total freshwater production at each level (kg/h);
L-average latent heat of vaporization of fresh water (kcal/kg).
The above formula can be used to obtain the circulating brine flow rate under certain fresh water production requirements.
Salt balance FCf = BCb
Water balance F(1-Cf) = D+ B(1-Cb)
In the formula,
Cf is the mass concentration of salt in raw water (kg/kg);
Cb-mass concentration of salt in discharged brine (kg/kg)
Substituting the concentration ratio α=Cb /Cf into the above two equations, we can get:
It can be seen that under the condition that the fresh water output is known, the flow rate F of supplementary raw water and the flow rate B of discharged brine are mainly determined by the concentration ratio of the system.
The concentration ratio refers to the ratio of the final brine concentration (total dissolved solids TDS) of the flash evaporation device to the replenishment seawater concentration (TDS). It is generally limited to scale prevention safety based on specific water quality conditions, and the salt discharge concentration generally cannot approach 70,000 mg/L .
For seawater desalination, there is no "single" best solution for the choice of technology. Instead, it should be based on the characteristics of each project and the actual conditions, including scale, energy costs, raw water quality, climatic conditions, and technical and safety requirements.
Generally speaking, reverse osmosis is suitable for independently established seawater desalination plants, but if there is a thermal power plant (latest nuclear power plant), thermal distillation technology is more economical and reliable.
The multi-stage flash evaporation method is not only used for seawater desalination, but has also been widely used in boiler water supply in thermal power plants and petrochemical plants, the treatment and recovery of industrial wastewater and mine brackish water, as well as the recovery of waste alkali liquor in the printing and dyeing industry and the papermaking industry.

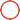 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 
